Using a Perceptron Neural Network for Binary Classification
- 2 minstldr; can we use a perceptron neural network to improve out application or infrastructure monitoring e.g. determine erroneous alerts or adjust our alerting thresholds automatically based on past events?
In this blog post, I will discuss my adventures implementing a binary classifier, for linearly separable data using an artificial neural network (ANN).
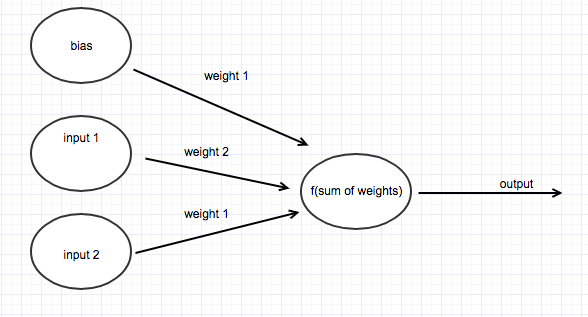
A neural network can be considered as a network of nodes connected by weights that takes ‘n’ number of inputs. See figure 1. To calculate the output of the neural network you multiply all the network inputs by their weights, sum them and pass them to an activation function which determines the output of the network. This is classification.
The inputs to the neural network can be considered the features or attributes of the object to classify. In our case, we will solve a simple problem. The logical ‘AND’ operator (Figure 2 truth table) as it is well-defined and involves two binary inputs.
| Input 1 | Input 1 | Expected Output |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
To train the neural network we adjust the weights. Will we use the Perceptron supervised learning method to train the network. This means for any two inputs we know what the expected output is and that as the algorithm is applied through a number of iterations which are called epoch the network converges towards a solution. This truth table above is the training set to be used by the Perceptron algorithm.
First, we need to define our activation function for calculating the output of the network. We will say if the sum of the inputs multiplied by their weights is more than 0.5 the network will output a 1, else 0. This is referred to as a unit step function.
To train the network will we do the following:
- Set the current weights of the network to random numbers.
- For each training set calculate the error by taking the expected result from the actual and adjust the weights accordingly by some percentage which is defined as the learning rate.
- Repeat steps 2 for 'n' epoch until the solution is solved. Not all solution are solvable with this network setup. Try XOR.
By doing this we can see that by setting all the weights to 0.2 it will solve the logical AND problem.
e.g. Input 1 = 1 Input 2 = 1 Bias = 1 output = (1 * 0.2) + (10.2) + (10.2) = 0.6 > 0.5 = 1
Whats next?
- Can we use this in our application or infrastructure monitoring to determine erroneous alerts or adjust our alerting thresholds automatically based on past events?
See a Python implementation of this network here.